In today's world, seven different generations are distinguished. In this article, we will study their differences, main characteristics as well as the stakes that govern each one at both economic and social levels.
Since always, individuals present in society are divided into different generations, which has an impact on a large number of domains, such as the choice of policies in one sector of activity or still the way companies will behave when elaborating their marketing strategy.
It has become evident that every generation possesses its own vision of the world, its way of understanding the work world but also its manner of consuming. Expectations in a large number of domains are clearly not the same and for this reason, it demands constant adaptation from companies as well as policies which must be able to please everyone and bring solutions to each person's problems.
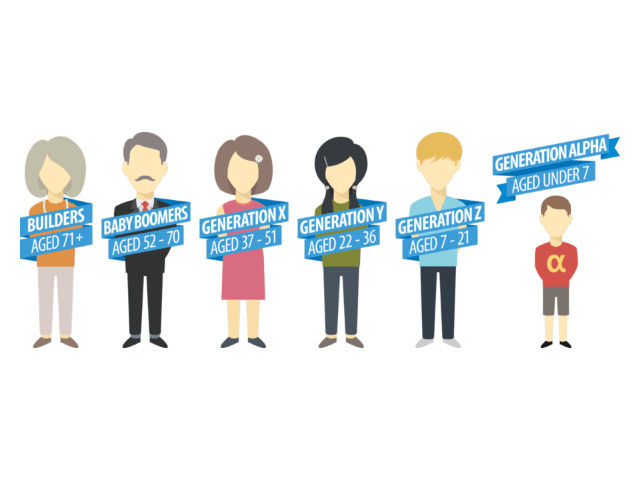
Study of the 7 generations
1928-1945: the Builders
These are individuals who grew up during World War II. Today, they often appear as a silent and discreet generation respectful of established order.
It is about individuals who have necessarily been very impacted by the consequences of war, with all that this has implied, such as rebuilding the country in particular. The Great Depression was also part of their daily life; they are therefore more economical consumers than others, they only buy when it is strictly necessary, they value saving.
For them, social norms and authority were very important. Men and women were not equal, especially in terms of work.
1946-1964 : The Baby-boomers
It is about individuals born after the war, for them economic prosperity was at its peak for years. They are often linked to strong social movements, particularly because they wanted to shake things up in order to live better, with more equality. Civil rights and feminism developed a lot during this period, with an important role also in the development of culture.
For these individuals, access to employment has been greatly facilitated, and they exert very strong pressures on everything related to retirement pensions and even more so on healthcare.
1965-1980 : Generation X
These are individuals whose parents worked a lot outside, both parents most often. Today's youngest see this generation as more independent than others but also more cynical.
They tend to hold their elders responsible who have "had everything," while life has often been more difficult for them, with a significant rise in unemployment rates across the entire territory.
They have otherwise been witnesses to a great number of changes, especially concerning the use of new technologies in companies but also at home.
They have for a majority fear that their retirement is clearly threatened by various reforms; they find themselves in a system which has changed completely over the space of just a few years.
On a social level, Generation X gradually places more importance on leisure activities and family in general. They want an equilibrium between private life and professional life, which will also be found among subsequent generations.
1981-1996 : Generation Y - millennials
They are undoubtedly born at a time when technological innovations appeared head-on in the world. They have known the appearance of internet and especially its development and implementation within homes.
For other generations, Generation Y is rather egocentric and very connected.
At an economic level, millennials are more indebted than others, as the cost of studies can be very high. They also suffer from precarious employment and perform small jobs that turn out to be only alimentary.
As next generations, millennials are more engaged on environmental and ecological issues. They are also very present on certain social networks, such as Facebook in particular.
1997-2012 : Generation Z
These are the first to have seen the light in a society exclusively based on the digital world or almost. They possess very high expectations, particularly concerning ecology but also the work world. They do not want to reproduce a scheme where they would have to be content with purely alimentary jobs; they want to find an occupation that really pleases them and within which they could engage in a more active way.
Globally, it is also a generation that worries about the country's future, especially at an economic level. Very active in social movements, she fights more easily for gender equality, in the world of work, as well as for cultural diversity. More awareness of problems on the job too, such as depression.
- How does generation Z consume music? - Between simplicity and instantness
- Which Factors Motivate Generation Z to Pay for and Recommend Premium Streaming Music?
2013-2025 : Generation Alpha
Individuals grow up in technology. A true transformation has taken place, both socially as well as in technological and professional domains. Jobs offered change drastically; many new jobs are appearing gradually, more related to the net, social networks, content creation. The Alpha generation is resolutely creative, it needs recognition and autonomy.
They will have to face a series of environmental protection issues.
2025 and beyond : Beta Generation
This is a generation that will evolve with AI, with all that this implies for society, work, and family life. They will have to endure much pressure especially at an environmental level, and they must find more relevant ways to improve things and get them moving.
It is a more "international" generation that will have the desire to exchange, share, discover cultures. Cultural identity will probably be less defined.
Each generation is very different, whether in terms of culture, technology, work relationships, or environmental relationships. Each has its own challenges to overcome, and solutions provided always have more or less significant consequences for subsequent generations.